Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
In today's rapidly evolving technology landscape, the role of Solid State Relays (SSRs) has become increasingly significant. Leading expert in automation, Dr. Jane Smith, once stated, "Choosing the right Solid State Relay can make all the difference in your system's efficiency and reliability." This statement emphasizes the need to understand different SSR types for various applications.
Solid State Relays offer distinct advantages over traditional electromechanical relays. They provide faster switching times and enhanced durability. In many cases, SSRs can operate in extreme conditions, ensuring dependability where conventional relays may fail. However, selecting the appropriate SSR is not always straightforward. Each application may reveal unforeseen challenges, like thermal management or voltage requirements.
As we delve into the best types of Solid State Relays for various uses, we must consider both their strengths and limitations. These components are essential in sectors ranging from industrial automation to renewable energy. Understanding both common and less effective choices can lead to improved outcomes while helping us avoid potential pitfalls. Thus, exploring this topic is crucial for optimizing performance and achieving success in your projects.
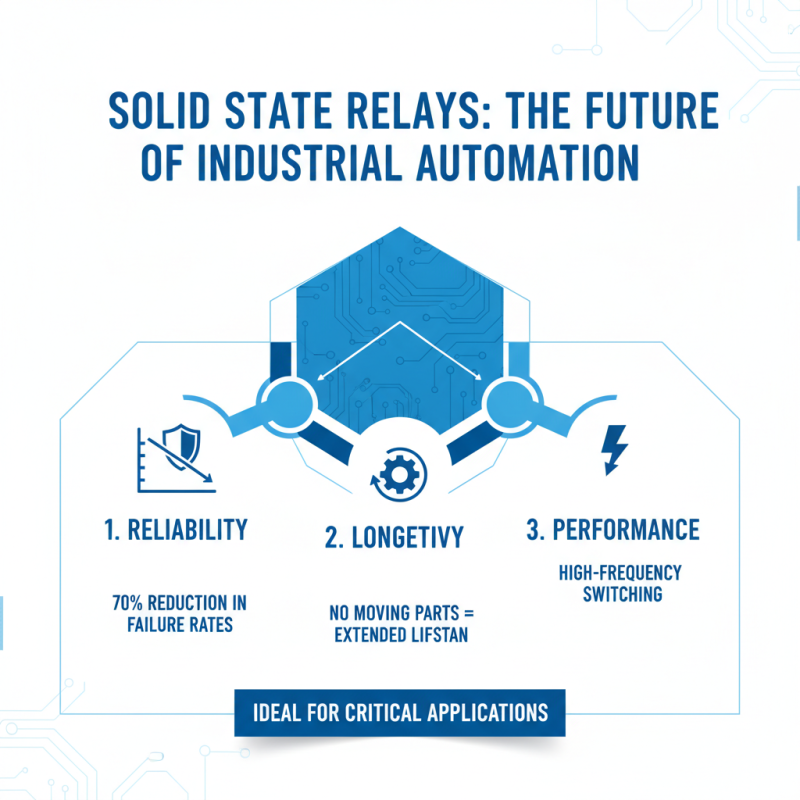
Solid State Relays (SSRs) offer diverse applications in industrial control and automation. With their solid-state construction, they provide a reliable alternative to traditional electromechanical relays. In fact, according to industry research, SSRs can reduce failure rates by up to 70%. This reliability makes them ideal for high-frequency switching tasks.
There are several types of SSRs based on their control mechanisms and load types. Opto-isolated SSRs are commonly used due to their ability to isolate control and load circuits. They excel in applications requiring low-power control and high-voltage loads, such as heating systems. On the other hand, zero-crossing SSRs are perfect for AC applications as they minimize electrical noise during operation, which is crucial in sensitive environments. According to market analysis, these types dominate about 55% of the SSR market due to their efficiency.
However, selecting the right SSR can be challenging. Factors like load characteristics and required switching speeds need careful consideration. Some SSRs might not perform adequately under extreme temperature conditions. Additionally, the total cost of ownership should include maintenance and potential downtime. Each application presents unique challenges; understanding these nuances is vital for optimal relay selection.
When choosing a solid state relay (SSR), consider key features like current rating, voltage range, and switching speed. Current ratings typically range from a few amperes to hundreds. For applications requiring high power, select SSRs with a higher ampacity to avoid overheating. Look into voltage ratings as well. Many SSRs can handle voltages from 24V to over 600V, which is essential for compatibility with your system.
Switching speed is crucial. Some SSRs can switch in milliseconds or less, making them suitable for applications needing rapid on-off cycling. For example, a report from the Semiconductor Industry Association states that SSRs with fast switching capabilities improve efficiency in automation systems by up to 30%. However, not all applications require ultra-fast response times. For simpler tasks, a standard speed might suffice, saving costs.
Thermal performance is another vital consideration. Heat sinking is often necessary to prevent thermal runaway. Even with the best SSRs, inadequate heat management can lead to failure. It's essential to evaluate your system's heat dissipation requirements before finalizing your choice. Another factor to keep in mind is the potential for electromagnetic interference (EMI). Poorly shielded SSRs may disrupt sensitive equipment, warranting additional shielding measures in your design.
This chart displays the maximum load current capabilities of various types of solid state relays, which is a crucial factor when selecting a suitable relay for your specific applications.
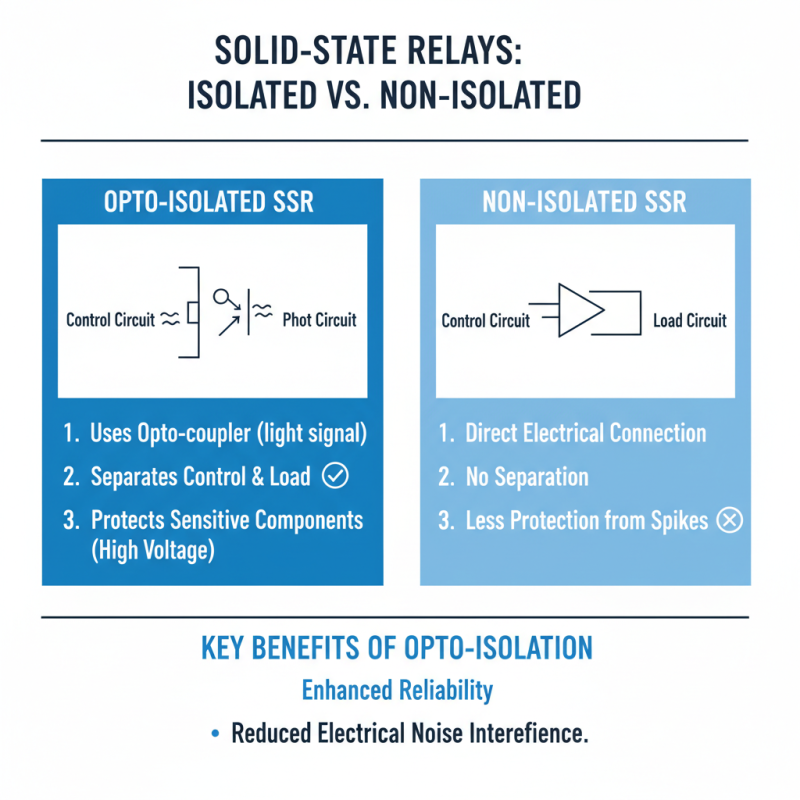
When choosing solid state relays (SSRs) for your projects, understanding the differences between opto-isolated and non-isolated types is crucial. Opto-isolated SSRs use an opto-coupler to separate the control signal from the load circuit. This provides the benefit of protecting sensitive components from high voltages. The isolation can enhance reliability, especially in environments with electrical noise.
On the other hand, non-isolated solid state relays have a direct connection between input and output. They often simplify the circuit design and reduce costs. However, they don't provide electrical isolation. This leaves your control circuit vulnerable to surges, which could lead to failures.
Tip: When selecting an SSR, consider the operating environment. If interference is a concern, opto-isolated types may serve you better.
Keep in mind that while opto-isolated relays offer more protection, they can be more expensive. It's essential to weigh the pros and cons based on your specific needs.
Tip: Ensure that your selected SSR can handle the load current and voltage. Underestimating requirements can lead to reliability issues. It's a simple detail but can significantly impact performance.
Solid state relays (SSRs) are crucial in industrial automation. They enhance efficiency and reliability in controlling electrical loads. SSRs provide fast switching capabilities and are resistant to vibration and shock. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global SSR market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.3% through 2026. This growth indicates a rising demand for efficient control solutions in various sectors.
SSRs are widely used in applications like heating, lighting, and motor control. They help in precise temperature regulation in industrial ovens. Their silent operation offers advantages in environments where noise pollution is a concern. Moreover, SSRs handle high currents without mechanical wear, extending service life. However, SSRs can generate heat, requiring careful thermal management.
Tips: Always consider the load type when selecting an SSR. Resistive loads differ from inductive loads. Improper selection can lead to malfunction. Additionally, ensure that the relay matches your system voltage and current ratings. Test and validate SSR performance in real-world conditions before full-scale implementation.
Proper installation and maintenance of solid state relays (SSRs) are crucial for optimal performance. According to a recent industry report, poorly installed SSRs can lead to a 20% efficiency loss in applications. Correct wiring and configuration are essential. Pay attention to voltage ratings and heat dissipation needs during installation. Misjudging these can lead to overheating. Records show that 25% of SSR failures stem from inadequate heat management.
Routine maintenance is vital. Check connections regularly. Loose wires can compromise functionality. It’s equally important to monitor ambient temperatures. Excessive heat can shorten the lifespan of an SSR. An alarming statistic indicates that 40% of unexpected relay failures result from thermal overload. Using heat sinks can extend the relay’s life significantly. However, many overlook this aspect.
Documentation is often neglected. Keeping track of installation details aids future troubleshooting. Repair errors often arise from miscommunication about new setups. Simple notes can clarify complex installations. Continuous learning about SSR operational limits is essential. Failure to do so can lead to costly mistakes. Staying informed can enhance reliability and performance in the long run.
